本文记录我对MyBatis学习系列之MyBatis与Spring结合实现原理的理解(基于MyBatis 3.4,Spring 3.2,MyBatis-Spring 1.3版本)。
前言
在Spring与MyBatis结合使用时,applicationContext.xml的配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd">
<!-- 支持注解配置bean -->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<!--使用annotation 自动注册bean,并检查@Required,@Autowired的属性已被注入-->
<!-- base-package为需要扫描的包(含所有子包) -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.michael"/>
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:/config/database.properties</value>
<!--要是有多个配置文件,只需在这里继续添加即可 -->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="poolDataSource" abstract="true">
<property name="maxActive" value="500"/> <!-- 连接池的最大数据库连接数。设为0表示无限制。 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="100"/> <!-- 初始化连接数量 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="50000"/> <!-- 最大建立连接等待时间。如果超过此时间将接到异常。设为-1表示无限制。 -->
<property name="removeAbandonedTimeout" value="60"/> <!--自我中断时间秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="30000"/> <!--连接的超时时间,默认为半小时。-->
<property name="minIdle" value="100"/> <!-- 最小等待连接中的数量,设 0 为没有限制 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="30000"/> <!-- #运行判断连接超时任务的时间间隔,单位为毫秒,默认为-1,即不执行任务。 -->
<property name="jmxEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 注册池JMX。的默认值是true。-->
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="false"/> <!--默认值是false,当连接池中的空闲连接是否有效 -->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="true"/> <!-- 默认值是true,当从连接池取连接时,验证这个连接是否有效-->
<property name="validationInterval" value="30000"/> <!--检查连接死活的时间间隔(单位:毫妙) 0以下的话不检查。默认是0。 -->
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false"/> <!--默认值是flase,当从把该连接放回到连接池的时,验证这个连接是 -->
<property name="validationQuery" value="select 1"/> <!--一条sql语句,用来验证数据库连接是否正常。这条语句必须是一个查询模式,并至少返回一条数据。可以为任何可以验证数据库连接是否正常的sql-->
<property name="logAbandoned" value="false"/> <!--是否记录中断事件, 默认为 false-->
<property name="removeAbandoned" value="true"/> <!-- 是否自动回收超时连接-->
<!--这些拦截器将被插入到链中的一个java.sql.Connection对象的操作都是以拦截器。默认值是空的。
预定义的拦截器:
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.interceptor.ConnectionState - 跟踪自动提交,只读目录和事务隔离级别。
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.interceptor.tatementFinalizer - 跟踪打开的语句,并关闭连接时返回到池中。-->
<property name="jdbcInterceptors" value="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.interceptor.ConnectionState;org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.interceptor.StatementFinalizer"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource" destroy-method="close" parent="poolDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatisStudy?characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=yes" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="" />
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--dataSource属性指定要用到的连接池-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--configLocation属性指定mybatis的核心配置文件-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:config/Configuration.xml" />
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:com/michael/mapper/*.xml" />
</bean>
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.michael.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
其中与MyBatis加载相关的是id为sqlSessionFactory和id为userMapper的两个Bean。顾名思义,SqlSessionFactoryBean是用来创建SqlSessionFactory对象的,MapperFactoryBean是用来创建mapper接口对应的代理对象的,SqlSessionFactory是使用MyBatis的基础,下面就从这个类的实现开始看起。
SqlSessionFactoryBean创建
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}
}
可以看到,SqlSessionFactoryBean是一个InitializingBean,在其被Spring IOC容器初始化的时候其afterPropertiesSet方法会被调用,其主要作用就是建立SqlSessionFactory对象,用来操作MyBatis,之后可以通过其getObject方法来获取这个SqlSessionFactory对象。下面我们就来看下SqlSessionFactory对象的构建过程。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
/**
* Build a {@code SqlSessionFactory} instance.
*
* The default implementation uses the standard MyBatis {@code XMLConfigBuilder} API to build a
* {@code SqlSessionFactory} instance based on an Reader.
* Since 1.3.0, it can be specified a {@link Configuration} instance directly(without config file).
*
* @return SqlSessionFactory
* @throws IOException if loading the config file failed
*/
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) { // 如果之前configuration对象已经被创建过
configuration = this.configuration;
if (configuration.getVariables() == null) {
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
configuration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) { // 使用XMLConfigBuilder解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
}
configuration = new Configuration();
if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
}
}
// 如果在SqlSessionFactoryBean创建的时候设置了下面这些属性,则直接将其添加到configuration对象中
if (this.objectFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectFactory(this.objectFactory);
}
if (this.objectWrapperFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectWrapperFactory(this.objectWrapperFactory);
}
if (this.vfs != null) {
configuration.setVfsImpl(this.vfs);
}
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
String[] typeAliasPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeAliasesPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeAliasPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(packageToScan,
typeAliasesSuperType == null ? Object.class : typeAliasesSuperType);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for aliases");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
for (Class<?> typeAlias : this.typeAliases) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
for (Interceptor plugin : this.plugins) {
configuration.addInterceptor(plugin);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
}
}
}
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
String[] typeHandlersPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeHandlersPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeHandlersPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(packageToScan);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for type handlers");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
for (TypeHandler<?> typeHandler : this.typeHandlers) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
}
}
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {//fix #64 set databaseId before parse mapper xmls
try {
configuration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
if (this.cache != null) {
configuration.addCache(this.cache);
}
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse(); // 使用xmlConfigBuilder解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的配置
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
if (this.transactionFactory == null) {
// 使用SpringManagedTransactionFactory代替MyBatis提供的TransactionFactory
this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory();
}
configuration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource));
// 如果SqlSessionFactoryBean中的mapperLocations属性被设置了的话
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
}
// 创建SqlSessionFactory对象
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
}
从上面代码介绍中可以看到,尽管我们还是习惯于将MyBatis的配置与Spring的配置独立出来,但是,这并不代表Spring中的配置不支持直接配置,也就是说,在上面提供的示例中,完全可以取消配置中的configLocation属性,而把mybatis中的属性配置(比如typeAliasPackage)直接写在sqlSessionFactoryBean中。
由于sqlSessionFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,所以当通过getBean方法获取对应实例时,其实是获取该类的getObject()函数返回的实例,也就是获取初始化后的sqlSessionFactory属性。
MapperFactoryBean创建
单独使用MyBatis时调用数据库接口的方式是:
UserMapper usermapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
而在这一过程中,其实是MyBatis在获取映射的过程中根据配置信息为UserMapper类型动态创建了代理类。而对于Spring的创建方式:
UserMapper userMapper = (UserMapper)context.getBean("userMapper");
Spring中获取的名为userMapper的bean(实际是一个MapperFactoryBean类的对象),其实是与单独使用MyBatis完成了一样的功能,那么我们可以推断,在bean的创建过程中一定是使用了MyBatis的原生方法sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class)进行了再一次封装,下面就来看看怎么实现的:
applicationContext.xml中的MapperFactoryBean类的配置:
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.michael.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
可知实例化一个userMapper对象之后,MapperFactoryBean中的setSqlSessionFactory和setMapperInterface两个方法会被分别调用设置其中的sqlSessionFactory和mapperInterface属性。
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
private SqlSession sqlSession; // 底层实现是SqlSessionTemplate,多个SqlSessionTemplate共用一个SqlSessionFactory
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (!this.externalSqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
public void setMapperInterface(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
}
MapperFactoryBean还实现了InitializingBean接口,在其属性被设置完之后,其afterPropertiesSet方法会被调用,现在就来看看afterPropertiesSet方法中做了什么:
public abstract class DaoSupport implements InitializingBean {
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
// Let abstract subclasses check their configuration.
checkDaoConfig();
// Let concrete implementations initialize themselves.
try {
initDao();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}
}
从其中的checkDaoConfig()方法开始看起:
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
// 进行mapperInterface属性不为空的验证
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
// 将mapperInterface在mapperRegistry中注册
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
}
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
// 进行sqlSession不为空的验证
notNull(this.sqlSession, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required");
}
}
可见checkDaoConfig()方法的主要作用就是检查sqlSession与mapperInterface两个属性已经被设置,并在Configuration对象中注册mapperInterface接口。
对于DaoSupport.afterPropertiesSet中使用的initDao方法,DaoSupport类中的实现为空,其子类中也并没有重写此方法,所以并没有做任何实质性工作。
到这里MapperFactoryBean对象的实例化工作就已经进行完了,由于MapperFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,所以我们通过getBean()获取到的对象实际是其getObject()函数返回的实例:
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
// 可以看到获取的代理实现实际是通过SqlSessionTemplate.getMapper方法完成的
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
}
在分析使用SqlSessionTemplate.getMapper方法获取实际代理对象之前,再来分析一种用来在applicationContext.xml中注册mapperinterface的更常用的实现,即通过MapperScannerConfigurer注册:
注释掉原来的配置:
<!--<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">-->
<!--<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.michael.mapper.UserMapper"/>-->
<!--<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>-->
<!--</bean>-->
添加下面的配置:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value = "com.michael.mapper"></property>
<!-- 这样配置以后,只有当真正去用mybatis的时候,才会去初始化SqlSessionFactoryBean-->
<!--否则会导致配置文件中的${driverClassName}变量没有被替换成真正的值之前,-->
<!--org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer 已经开始初始化SqlSessionFactoryBean了,-->
<!--会导致加载报错,项目无法启动,报Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction; -->
<!--nested exception is java.sql.SQLException: ${driverClassName}这个错误。-->
<!--如果不设置此属性,默认使用的sqlSessionFactory属性名字是"sqlSessionFactory"-->
<!--<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>-->
</bean>
添加的配置的作用是自动扫描给定包下的mapperInterface类并完成注册,mapperInterface无需任何特殊操作,注册后的bean名称默认为mapperInterface类名的首字母小写,其余不变(比如UserMapper bean名称为userMapper);当然也可以在mapperInterface接口上添加@Component注解为其指定bean名称。下面就来分析自动扫描的实现原理:
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
}
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
可见MapperScannerConfigurer实现了四个接口,在MapperScannerConfigurer Bean被实例化过后,这四个接口对应的方法会被依次调用,其中ApplicationContextAware与BeanAware接口的回调方法分别用来设置MapperScannerConfigurer中的applicationContext和beanName属性,InitializingBean对应的afterPropertiesSet回调方法是先于BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对应的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法发生的,来看看扫描mapperInterface接口并在Configuration中注册的功能是不是在afterPropertiesSet中发生的:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(this.basePackage, "Property 'basePackage' is required");
}
显然不是,afterPropertiesSet方法中仅仅检测了basePackage属性不为空,那么继续来看postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法:
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
}
可以看到代码实现中正是完成了对指定路径扫描的逻辑,接下来就来对这个方法进行详细分析。
MapperScannerConfigurer.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry中processPropertyPlaceHolders方法分析:
根据方法注释给我们的提示,这个方法是为了防止MapperScannerConfigurer从配置文件中读取的属性值未被初始化的情况,比如这样:
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:/config/database.properties</value>
<value>classpath:/config/redis.properties</value>
<!--要是有多个配置文件,只需在这里继续添加即可 -->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value = "${basePackage}"></property>
</bean>
这样配置的话就会出现basePackage属性没有被加载的情况。为什么会出现这种情况呢?因为解析配置文件中属性值的bean是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,它是一个我们自定义注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,而MapperScannerConfigurer是一个我们自定义注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,所以MapperScannerConfigurer回调会优先于PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer回调执行。
可以确定的BeanFactoryPostProcessor回调方法执行顺序(通过Spring源码中AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)确定):
- 执行系统预定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
- 执行我们自定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
- 执行系统预定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory方法。
- 执行我们自定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory方法。
- 执行系统预定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory方法。
- 执行我们自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory方法(根据实现的Ordered接口和配置文件中的顺序决定执行顺序)。
要想防止这种情况,我们需要这样配置MapperScannerConfigurer:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value = "${basePackage}"></property>
<property name="processPropertyPlaceHolders" value="true" />
</bean>
通过这样配置,在执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法时就会执行processPropertyPlaceHolders方法,就是在这个方法中解决的这个情况:
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
/*
* BeanDefinitionRegistries are called early in application startup, before
* BeanFactoryPostProcessors. This means that PropertyResourceConfigurers will not have been
* loaded and any property substitution of this class' properties will fail. To avoid this, find
* any PropertyResourceConfigurers defined in the context and run them on this class' bean
* definition. Then update the values.
*/
private void processPropertyPlaceHolders() {
// 加载applicationContext.xml中的PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean
Map<String, PropertyResourceConfigurer> prcs = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(PropertyResourceConfigurer.class);
if (!prcs.isEmpty() && applicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
// 获取当前类MapperScannerConfigurer的BeanDefinition,此时其中basePackage属性并没有被设置
BeanDefinition mapperScannerBean = ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext)
.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(beanName);
// PropertyResourceConfigurer does not expose any methods to explicitly perform
// property placeholder substitution. Instead, create a BeanFactory that just
// contains this mapper scanner and post process the factory.
// 使用DefaultListableBeanFactory模拟Spring中的环境来进行后处理器的调用,之后此beanFactory便失效
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
factory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, mapperScannerBean);
// 使用处理器找出mapperScannerBean中的basePackage属性并替换
for (PropertyResourceConfigurer prc : prcs.values()) {
prc.postProcessBeanFactory(factory);
}
PropertyValues values = mapperScannerBean.getPropertyValues();
// 由于当前MapperScannerConfigurer对象是在mapperScannerBean中的basePackage属性被替换之前创建的
// 所以替换之后要重新设置此对象的属性
this.basePackage = updatePropertyValue("basePackage", values);
this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName = updatePropertyValue("sqlSessionFactoryBeanName", values);
this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName = updatePropertyValue("sqlSessionTemplateBeanName", values);
}
}
}
MapperScannerConfigurer扫描过程分析:
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
// 设置我们在MapperScannerConfigurer bean文件中配置的属性
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
// 属性设置后通过registerFilters代码中生成的过滤器来控制扫描结果
scanner.registerFilters();
// 根据我们提供的包名进行扫描
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
}
下面来看具体的扫描过程:
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner extends ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider {
/**
* Perform a scan within the specified base packages.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
* @return number of beans registered
*/
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
// 记录扫描之前注册的bean数量
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
// 扫描后注册的bean数量-扫描前注册的bean数量即为扫描到的bean数量
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
/**
* Perform a scan within the specified base packages,
* returning the registered bean definitions.
* <p>This method does <i>not</i> register an annotation config processor
* but rather leaves this up to the caller.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
* @return set of beans registered if any for tooling registration purposes (never {@code null})
*/
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// 扫描basePackage路径下java文件
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
}
public class ClassPathMapperScanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner {
@Override
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
}
到此为止Mapper接口的注册过程就分析完成了,主要功能就是构造了与mapperInterface接口对应的MapperFactoryBean类的BeanDefinition的创建,并在Configuration对象中注册。
注意这里只是完成了BeanDefinition的注册,并没有生成实际的mapper代理对象,再次重申一下,由于MapperFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,所以我们通过getBean()获取到的对象实际是其getObject()函数返回的实例:
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
// 可以看到获取的代理实现实际是通过SqlSessionTemplate.getMapper方法完成的
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
}
每个mapper代理对象含有一个自己的SqlSessionTemplate对象,这些SqlSessionTemplate对象引用了一个共同的SqlSessionFactory对象。
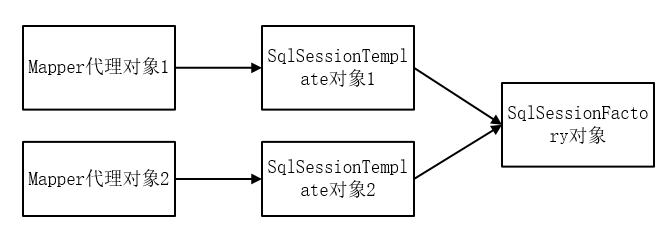
接下来继续分析实际mapper接口代理对象的构建过程。
SqlSessionTemplate.getMapper(Class type)生成实际mapper接口代理对象
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
// 可以看到获取的代理实现实际是通过SqlSessionTemplate.getMapper方法完成的
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
}
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
}
public class Configuration {
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
}
public class MapperRegistry {
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// MapperProxy中持有的SqlSession对象实际是一个SqlSessionTemplate类对象
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
}
最终获得的代理对象中持有的invocationHandler是一个MapperProxy类对象,其中引用的SqlSession对象是一个SqlSessionTemplate类的实例。
我在之前的博客MyBatis学习系列之MyBatis的SqlSession执行流程分析中分析到了SqlSession对象在多线程使用时不是线程安全的,在与Spring结合的过程中使用MyBatis时我们使用的单例mapper对象是可能在多线程情况下被操作的,那么线程安全问题是怎么解决的呢?下面就来分析这个问题。
mapper接口代理对象的方法执行过程
上面已经说过mapper接口代理对象持有的invocationHandler是一个MapperProxy类的实例对象,那么就从MapperProxy.invoke()方法开始分析:
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession; // 实际是一个SqlSessionTemplate类对象
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
public class MapperMethod {
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 使用sqlSession进行实际的数据库操作
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
}
接下来介绍实际对数据库进行操作的sqlSession.selectOne()方法(这里的sqlSession实际是一个SqlSessionTemplate类对象),在继续向下分析之前,先来看下SqlSessionTemplate的创建过程:
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {
// applicationContext中配置的sqlSessionFactory,多个SqlSessionTemplate共用一个
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private final ExecutorType executorType;
// 每个SqlSessionTemplate有自己的sqlSessionProxy对象
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy; // 动态代理对象
private final PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator;
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
// 默认用的是ExecutorType.SIMPLE,SimpleExecutor实现
this(sqlSessionFactory, sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getDefaultExecutorType());
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType) {
this(sqlSessionFactory, executorType,
new MyBatisExceptionTranslator(
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(), true));
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
// 动态代理,invocationHandler为SqlSessionInterceptor类对象
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
}
public class Proxy implements java.io.Serializable {
@CallerSensitive
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
接下来看selectOne()方法实现:
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement) {
// 调用SqlSessionInterceptor.invoke()方法
return this.sqlSessionProxy.<T> selectOne(statement);
}
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 先获取sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
// 接下来就是使用真正的sqlSession.selectOne方法进行查询的过程了,之前的博客中介绍过,不再分析
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
}
public final class SqlSessionUtils {
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
// 线程初次调用这个方法时返回null,线程+sessionFactory对象——>决定一个线程对应的SqlSessionHolder对象
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
// 线程初次调用时返回值为null,发现session为null之后就会在TransactionSynchronizationManager中为此线程创建
// 其对应的sessionHolder对象,之后再使用时就可以直接获取啦
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
// 线程初次调用时会为此线程建立自己的sqlSession,也就是说实质上每个线程有自己的sqlSession对象
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
// 建立完sqlSession之后要将其在TransactionSynchronizationManager中保存,以便此线程之后使用时获取
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
// 使用SpringManagedTransactionFactory将事务交给Spring进行管理
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
// 使用SqlSessionHolder包装SqlSession对象
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
// 重点!!!将sessionFactory与holder的对应关系设置到TransactionSynchronizationManager中的ThreadLocal变量中
// 以便此线程之后使用此SqlSessionHolder对象时可以再次获取到
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
// 这句代码的作用是???
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
}
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
}
}
}
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 注意这里使用的TransactionFactory是SpringManagedTransactionFactory
// 就是因为使用了这个SpringManagedTransactionFactory才做到了将事务交由Spring管理
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
分析完上述代码之后,我们可以看到SqlSessionTemplate在执行的过程中会通过其内部的代理对象为每个线程生成自己的SqlSession对象并保存在TransactionSynchronizationManager中的ThreadLocal变量中,就是通过动态代理的设计模式加上ThreadLocal方式完成了线程与SqlSession对象之间的对应,实现了MyBatis与Spring之间的集成。
SpringManagedTransaction如何将事务交由Spring处理
我们知道Spring与MyBatis结合之后是会将事务交由Spring进行处理的,这是通过SpringManagedTransaction来实现的,sqlSession在执行时使用的Connection对象是通过SpringManagedTransaction.getConnection()方法来实现的,我们就从这个方法开始分析:
public class SpringManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private Connection connection;
public SpringManagedTransaction(DataSource dataSource) {
notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 之前没创建过Connection才创建新的Connection
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
}
private void openConnection() throws SQLException {
// 获取数据库连接
this.connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.dataSource);
this.autoCommit = this.connection.getAutoCommit();
// 判断获取到的连接是不是已经开启了事务的
this.isConnectionTransactional = DataSourceUtils.isConnectionTransactional(this.connection, this.dataSource);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug(
"JDBC Connection ["
+ this.connection
+ "] will"
+ (this.isConnectionTransactional ? " " : " not ")
+ "be managed by Spring");
}
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
// 只有在事务是由sqlSession开启的才提交,否则不进行任何操作(比如在事务是由Spring开启的情况下)
if (this.connection != null && !this.isConnectionTransactional && !this.autoCommit) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
this.connection.commit();
}
}
}
public abstract class DataSourceUtils {
public static Connection getConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws CannotGetJdbcConnectionException {
try {
return doGetConnection(dataSource);
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new CannotGetJdbcConnectionException("Could not get JDBC Connection", ex);
}
}
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
// 可见获取Connection的过程是先尝试从TransactionSynchronizationManager中获取,获取不到才创建
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
conHolder.requested();
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource");
conHolder.setConnection(dataSource.getConnection());
}
return conHolder.getConnection();
}
// Else we either got no holder or an empty thread-bound holder here.
logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource");
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
logger.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for JDBC Connection");
// Use same Connection for further JDBC actions within the transaction.
// Thread-bound object will get removed by synchronization at transaction completion.
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
if (holderToUse == null) {
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}
else {
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
holderToUse.requested();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}
return con;
}
}
经过上述代码分析可知通过SpringManagedTransaction.getConnection方法获取数据库连接的过程是先通过TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource方法尝试获取,拿不到再创建。而在我之前的博客Spring学习系列之Spring事务处理机制的实现中分析到Spring在Service层开启事务之后会把当前线程对应的开启了事务的Connection对象封装成ConnectionHolder对象存入TransactionSynchronizationManager中,所以我们通过TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource方法获取到的就是这个已经开启了事务的Connection,就是通过这种方式实现了将事务交给Spring控制的,所以TransactionSynchronizationManager在Spring事务控制的过程中的地位也是很重要的,是MyBatis与Spring之间沟通的桥梁。
关于MyBatis与Spring结合实现原理就分析到这里。
(完)