本文记录我对Spring 事件处理机制的使用和实现原理的理解(基于Spring3.2版本)。
前言
Spring事件处理机制符合标准的Observer设计模式,由ApplicationEventPublisher、ApplicationEvent、ApplicationListener三个组件组成;顾名思义,ApplicationEventPublisher用来发布事件,可继承ApplicationEvent来定制我们自己的事件,ApplicationListener用来监听事件的发生,下面来看一个简单的使用示例:
// 定制事件
public class InitEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String data;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
*
* @param source the component that published the event (never {@code null})
*/
public InitEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
public InitEvent(Object source, String data) {
super(source);
this.data = data;
}
}
// 监听事件
public class InitEventListener implements ApplicationListener<InitEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(InitEvent event) {
System.out.println("接收到initevent:" + event.getData());
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-3.0.xsd">
<task:executor id="executor" pool-size="10" />
<!-- 名字必须是applicationEventMulticaster和messageSource是一样的,默认找这个名字的对象 -->
<!-- 名字必须是applicationEventMulticaster,因为AbstractApplicationContext默认找个 -->
<!-- 如果找不到就new一个,但不是异步调用而是同步调用 -->
<bean id="applicationEventMulticaster" class="org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster">
<!-- 注入任务执行器 这样就实现了异步调用(缺点是全局的,要么全部异步,要么全部同步(删除这个属性即是同步)) -->
<property name="taskExecutor" ref="executor"/>
</bean>
<bean class="mytests.events.InitEventListener"/>
</beans>
// 这里直接通过ApplicationContext发布事件,还可以通过实现接口ApplicationEventPublisherAware获取
// ApplicationEventPublisher对象来发布事件
public class PublishEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
context.publishEvent(new InitEvent("testEvent", "event"));
context.close();
}
}
执行结果:
接收到initevent:event
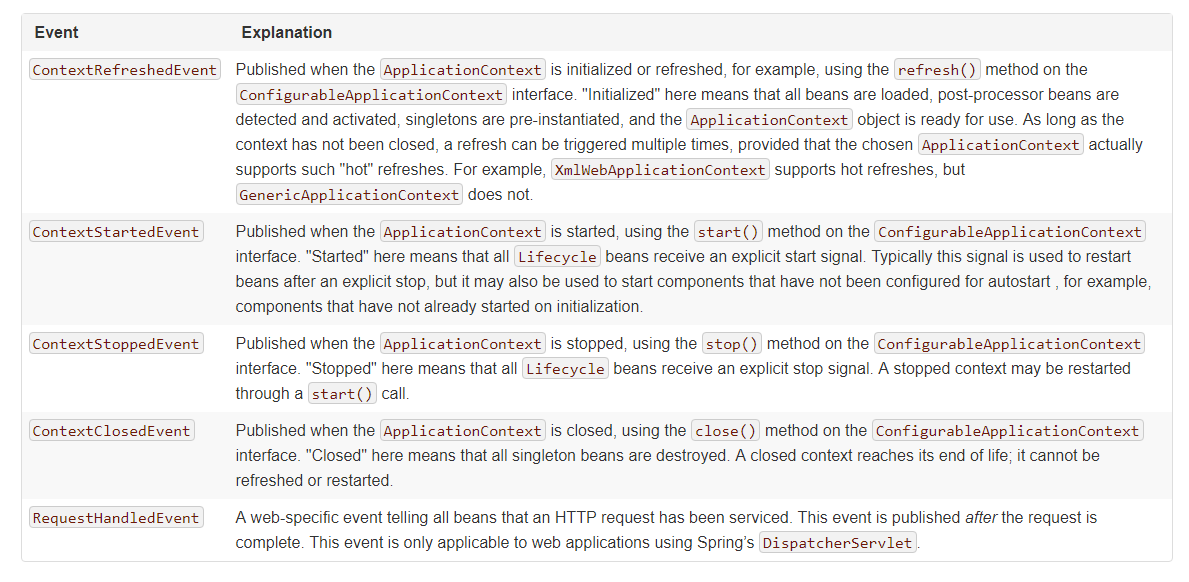
可以看到使用起来很简单,我们不仅可以监听自己自定义的事件,也可以监测一些Spring提供给我们的标准事件,比如通过监测ContextRefreshedEvent得知ApplicationContext已经初始化完成,Spring提供的标准事件图示如下:
下面就来看下Spring事件处理机制的实现原理。
实现原理
public class PublishEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:\\Users\\michael\\Desktop\\beans.xml");
context.publishEvent(new InitEvent("testEvent", "event"));
context.close();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
// 通过内置的ApplicationEventMulticaster发布事件,这里实际是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类对象
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(event);
if (this.parent != null) {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {
private Executor taskExecutor; // 使用线程池异步调用监听器的监听方法
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event) {
// 通过getApplicationListeners获取关注这个事件的所有监听器,挨个进行通知
for (final ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 如果指定了线程池
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
});
}
else { // 同步调用监听器监听方法
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
}
通过上面代码分析可以看到Spring事件发布-处理机制十分清晰,是典型的observer设计模式的实现。
还要注意的一点是我们在SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent方法中调用监听器的监听方法时有同步和异步两种方式,取决于我们是否在beans.xml中为SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster注入了Executor。当然除了在xml文件中注入Executor,还可以结合使用@EventListener、@Async来提供异步事件处理支持。
(完)