本文记录我对Spring AOP实现机制的使用和其实现原理的理解(基于Spring3.2版本)。
前言
在使用Spring框架进行web开发时,我们经常将SpringMVC(Spring框架的一个组件)、Spring框架(可使用除SpringMVC组件之外的其它一些组件提供的功能)、Mybatis等ORM框架结合起来使用,本篇博客就尝试分析一下在web环境下SpringMVC是如何初始化的。
下面以Tomcat作为web容器的例子进行分析。在Tomcat中,web.xml是应用的部署描述文件。在web.xml中常常看到与Spring相关的部署描述,如下面代码所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:/config/Spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextCleanupListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:config/SpringMVC-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
这里看到的部署描述是Spring MVC与Tomcat的接口部分。首先定义了两个servlet listener,就是由ContextLoaderListener监听器负责完成IOC容器在Web环境中的启动工作。context-param标签中的内容指定了Spring IOC容器读取Bean定义的XML文件的路径。
之后定义的Servlet对象DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC中的很重要的一个类,起着分发请求的作用。
DispatcherServlet与ContextLoaderListener提供了在Web容器中对Spring的接口,也就是说,这些接口与Web容器耦合是通过ServletContext来实现的。这个ServletContext为Spring的IOC容器提供了一个宿主环境,在宿主环境中,Spring MVC建立起一个IOC容器的体系。这个IOC容器体系是通过ContextLoaderListener的初始化来建立的,在建立起IOC容器的体系之后,把DispatcherServlet作为Spring MVC处理web请求的转发器建立起来,从而完成响应HTTP请求的准备。有了这些基本配置,建立在IOC容器基础上的Spring MVC就可以正常的发挥作用了。
下面我们就来看看IOC容器在Web容器中的启动过程以及DispatcherServlet是如何转发Web请求的。
IOC容器在Web环境中的启动过程
上面已经提到了IOC容器在Web容器中的启动是由ContextLoaderListener启动的,ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口,在web容器中对IOC容器初始化的过程就是在其回调方法contextInitialized的接口实现中完成的:
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
}
public class ContextLoader {
/**
* The root WebApplicationContext instance that this loader manages.
*/
private WebApplicationContext context;
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// 创建WebApplicationContext上下文,默认获得的是一个XmlWebApplicationContext对象
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
...
}
}
ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext方法中完成了两个IOC容器建立的基本过程,一个是在Web容器中建立起双亲IOC容器,另一个是生成相应的WebApplicationContext并将其初始化。在继续向下分析之前,先来看下WebApplicationContext接口的类层次关系:
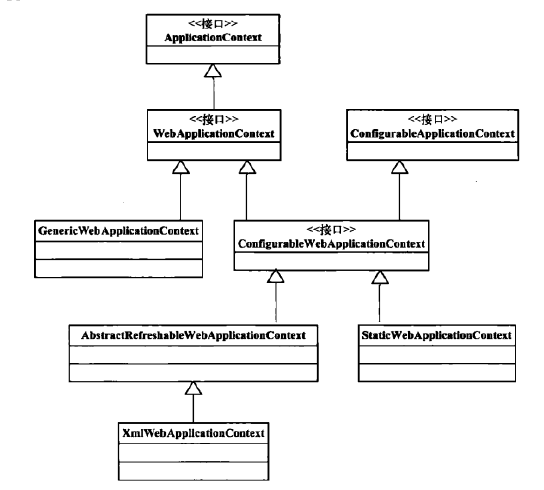
接下来看创建WebApplicationContext的createWebApplicationContext方法:
public class ContextLoader {
/**
* Instantiate the root WebApplicationContext for this loader, either the
* default context class or a custom context class if specified.
* <p>This implementation expects custom contexts to implement the
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} interface.
* Can be overridden in subclasses.
* <p>In addition, {@link #customizeContext} gets called prior to refreshing the
* context, allowing subclasses to perform custom modifications to the context.
* @param sc current servlet context
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// 决定创建哪种Context,默认是XmlWebApplicationContext
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
/**
* Return the WebApplicationContext implementation class to use, either the
* default XmlWebApplicationContext or a custom context class if specified.
* 返回要使用的WebApplicationContext的实现类,或者是指定的实现类,或者是默认的XmlWebApplicationContext
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the WebApplicationContext implementation class to use
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
}
public abstract class BeanUtils {
/**
* Instantiate a class using its no-arg constructor.
* 使用无参构造函数通过反射方式实例化一个类
* As this method doesn't try to load classes by name, it should avoid
* class-loading issues.
* <p>Note that this method tries to set the constructor accessible
* if given a non-accessible (that is, non-public) constructor.
* @param clazz class to instantiate
* @return the new instance
* @throws BeanInstantiationException if the bean cannot be instantiated
*/
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> clazz) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class must not be null");
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
return instantiateClass(clazz.getDeclaredConstructor());
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
获取到XmlWebApplicationContext之后再通过它在其configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法中来启动IOC容器,与在普通应用中启动IOC容器的方式类似,不同之处在于需要考虑Web容器的环境特点;比如各种参数的设置,IOC容器与Web容器ServletContext的结合等等,这也正是有了XmlApplicationContext之后还要设计XMLWebApplicationContext的目的。正是因为下面的代码将初始化好的XMLWebApplicationContext对象存入到ServletContext中,之后在DispatcherServlet中才可以通过ServletContext获取此XMLWebApplicationContext对象。
public class ContextLoader {
/**
* The root WebApplicationContext instance that this loader manages.
*/
private WebApplicationContext context;
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// 创建WebApplicationContext上下文,默认获得的是一个XmlWebApplicationContext对象
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
// 如果上下文还没有被初始化
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
// 载入根上下文的双亲上下文
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 对WebApplicationContext进行参数设置(比如双亲上下文、对ServletContext的引用等)
// 并通过对refresh方法的调用,重启整个IOC容器,就像一般的IOC容器初始化过程一样
// 此方法执行过后是可以通过WebApplicationContext.getServletContext()获取到servletContext对象的
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// 通过servletContext可以获得WebApplicationContext上下文
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
// IOC容器在web容器中启动,与在普通应用中启动IOC容器的方式类似,不同之处在于需要考虑Web容器的环境特点
// 比如各种参数的设置,IOC容器与Web容器ServletContext的结合等等
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
// Servlet <= 2.4: resort to name specified in web.xml, if any.
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getServletContextName()));
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
}
// 建立WebApplicationContext与ServletContext之间的互相引用关系
wac.setServletContext(sc);
// 获取WebApplicationContext中要加载的资源文件的位置,由web.xml中通过contextConfigLocation参数指定
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
// 在WebApplicationContext通过refresh初始化之前,如果定制了ApplicationContextInitializer,则执行
customizeContext(sc, wac);
// 真正的初始化操作,与之前博客介绍的IOC容器初始化过程是相同的,不再赘述
// 执行的实际是AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh方法
wac.refresh();
}
}
到此为止,IOC容器在Web容器中的启动过程已经分析完了,接下来就来分析DispatcherServlet转发Web请求的原理。
DispatcherServlet 初始化
DispatcherServlet是一个Servlet,Tomcat容器启动时会调用它的init方法对其进行初始化,先来看一下DispatcherServlet的继承类图:
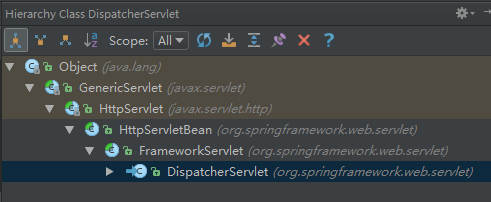
现在我们就从这个init方法开始进行分析:
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet
implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
/**
* Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and
* invoke subclass initialization.
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// 获取servlet的初始化参数,对Bean属性进行配置
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
// 调用子类的initServletBean进行具体的初始化
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
}
接下来的初始化过程发生在FrameworkServlet.initServletBean方法中,在这个初始化过程中,一个新的IOC容器上下文被建立起来,这个新的上下文被设置为根上下文的子上下文,被DispatcherServlet持有:
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean {
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 为此DispatcherServlet初始化一个新的web上下文
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
/**
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获取之前通过servletContext初始化的根WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
// 如果ServletContext中已经指定了WebApplicationContext
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
// 并没有为此servlet定义一个context实例,那就创建一个本地的
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
// 把当前建立的上下文存到ServletContext中去,注意使用的属性名是和当前servlet名相关的
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(WebApplicationContext parent) {
return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent);
}
// 为此servlet初始化一个WebApplicationContext,并指定其父AC为通过ContextLoaderListener创建的AC
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 为此servlet初始化一个WebApplicationContext,默认是XmlWebApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// 设置相关参数,比如设置父AC,此AC的资源文件的位置
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
//
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
ServletContext sc = getServletContext();
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
// Servlet <= 2.4: resort to name specified in web.xml, if any.
String servletContextName = sc.getServletContextName();
if (servletContextName != null) {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + servletContextName +
"." + getServletName());
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + getServletName());
}
}
else {
// Servlet 2.5's getContextPath available!
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()) + "/" + getServletName());
}
}
}
// 将WebApplicationContext与web环境结合
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
// 如果没有为此wac设置配置文件的位置的话,会默认使用servlet名称+ -servlet的后缀
// 比如dispatcher-servlet.xml,也就是这里设置的nameSpace
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
// 真正的初始化操作,与之前博客介绍的IOC容器初始化过程是相同的,不再赘述
// 执行的实际是AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh方法
wac.refresh();
}
}
到目前为止,DispatcherServlet的初始化就完成了,建立了一个属于它自己的IOC容器,还设置了父容器,将此容器在web环境下进行了一些适配;但是我们知道我们之后的请求是交给DisPatcherServlet进行分派的,但是上述初始化过程中并没有看到关于请求分派组件的初始化操作,这些组件的初始化操作是通过监听器回调的方式进行的:
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean {
/**
* ApplicationListener endpoint that receives events from this servlet's WebApplicationContext
* only, delegating to {@code onApplicationEvent} on the FrameworkServlet instance.
*
*/
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
// 在DispatcherServlet创建的WebApplicationContext可用之后,会调用此回调
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
/**
* Callback that receives refresh events from this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
* <p>The default implementation calls {@link #onRefresh},
* triggering a refresh of this servlet's context-dependent state.
* @param event the incoming ApplicationContext event
*/
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
// 调用子类DispatcherServlet的onRefresh方法
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
* DispatcherServlet对于SpringMVC框架组件的一些初始化操作
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 初始化支持国际化的LocaleResolver
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化支持request映射的HandlerMappings
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化支持视图生成的ViewResolver
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
}
需要注意的一点是:即使父WAC与DispatcherServlet建立起来的子WAC之间有bean的id相同,并且其属性被设置为单例的,这个Bean也会被初始化两次。比如ApplicationContext.xml与Dispatcher-servlet.xml中都配置了对Controller包的Component-Scan,那么这个包下的Controller类对象会被初始化两次。Controller中依赖的其它Bean(比如Service层的Bean),如果子WAC中没有,会使用父WAC中的对应bean来进行依赖注入。
SpringMVC Web请求转发原理
下面以initHandlerMappings方法来介绍DispatcherServlet实现web请求转发的原理:
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
/** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet */
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
/**
* Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class.
* <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace,
* we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
* 默认使用的HandlerMapping是BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
*/
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
// 导入所有的HandlerMapping Bean,这些Bean可以在当前的DispatcherServlet的IOC容器中,也可能在其双亲上下文中
// detectAllHandlerMappings默认设置为true,即默认的从所有的IOC容器中取
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else { // 从当前IOC容器中取
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
// 如果没有找到handlerMappings,那么需要为Servlet设定默认的handlerMappings
// 这些默认的值可以设置在DispatcherServlet.properties中
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
}
从initHandlerMappings方法中获得的HandlerMapping中已经配置好了URL与对应的Controller之间的关系,之后在处理web请求的时候通过DispatcherServlet的service方法调用相应HandlerMapping,根据请求url与Controller之间的关系来处理请求。在介绍请求具体如何被处理之前,以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例,先来看看HandlerMapping中的URL与Controller之间的对应关系是怎么建立起来的。
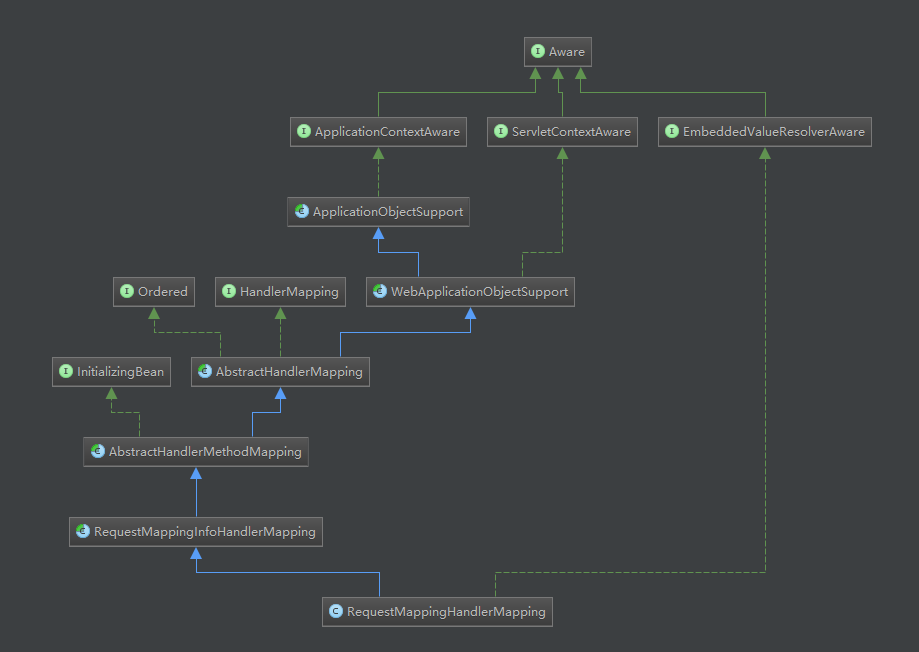
可以看到RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,当第一次尝试通过getBean方法从容器中获取RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象时,setApplicationContext回调方法就会被调用(对于ApplicationContextAware接口的回调,是通过ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization来调用的),我们就从这个回调方法开始分析:
public abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
/** ApplicationContext this object runs in */
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public final void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) {
// Reset internal context state.
this.applicationContext = null;
this.messageSourceAccessor = null;
}
else if (this.applicationContext == null) {
// Initialize with passed-in context.
if (!requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + requiredContextClass().getName() + "]");
}
this.applicationContext = context;
this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context);
// 初始化HandlerMapping中映射关系
initApplicationContext(context);
}
else {
// Ignore reinitialization if same context passed in.
if (this.applicationContext != context) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" +
this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]");
}
}
}
protected void initApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
initApplicationContext();
}
// 方法被子类覆盖
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
}
}
public abstract class WebApplicationObjectSupport extends ApplicationObjectSupport implements ServletContextAware {
/**
* Calls {@link #initServletContext(javax.servlet.ServletContext)} if the
* given ApplicationContext is a {@link WebApplicationContext}.
*/
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
super.initApplicationContext(context);
if (this.servletContext == null && context instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
this.servletContext = ((WebApplicationContext) context).getServletContext();
if (this.servletContext != null) {
initServletContext(this.servletContext);
}
}
}
}
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered {
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
// 获取所有IOC容器中注册的MappedInterceptor
detectMappedInterceptors(this.mappedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<MappedInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
mappedInterceptors.addAll(
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
getApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
}
上面介绍了RequestMappingHandlerMapping通过实现ApplicationContextAware接口回调实现了拦截器(即我们实现的SpringMVC的interceptor)的注册,RequestMappingHandlerMapping还实现了EmbeddedValueResolverAware和InitializingBean接口,都会有相应的回调,来看看这些回调里面都做了些什么:
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) {
this.embeddedValueResolver = resolver;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch) {
this.fileExtensions.addAll(this.contentNegotiationManager.getAllFileExtensions());
}
// 调用AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.afterPropertiesSet()方法
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* Expects a handler to have a type-level @{@link Controller} annotation.
* 根据是否含有Controller或RequestMapping来判断是否是handler
*/
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null) ||
(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) != null));
}
/**
* Uses method and type-level @{@link RequestMapping} annotations to create
* the RequestMappingInfo.
* @return the created RequestMappingInfo, or {@code null} if the method
* does not have a {@code @RequestMapping} annotation.
* @see #getCustomMethodCondition(Method)
* @see #getCustomTypeCondition(Class)
*/
@Override
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = null;
RequestMapping methodAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
if (methodAnnotation != null) {
RequestCondition<?> methodCondition = getCustomMethodCondition(method);
info = createRequestMappingInfo(methodAnnotation, methodCondition);
RequestMapping typeAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, RequestMapping.class);
if (typeAnnotation != null) {
RequestCondition<?> typeCondition = getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType);
info = createRequestMappingInfo(typeAnnotation, typeCondition).combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
}
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods = new LinkedHashMap<T, HandlerMethod>();
// 在其中保存访问路径与Controller中对应处理方法之间的关系
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, T>();
/**
* Detects handler methods at initialization.
*/
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
/**
* Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods.
* @see #isHandler(Class)
* @see #getMappingForMethod(Method, Class)
* @see #handlerMethodsInitialized(Map)
*/
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
// 找出当前子WAC容器中的所有bean的名称(默认detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts为false,
// 所以不会扫描父WAC中的bean)
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 判断此bean是不是一个handler
if (isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){
// 检测此handler中的所有的handler methods(通俗理解这里可以是检测Controller中所有RequestMapping对应的方法)
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
/**
* Look for handler methods in a handler.
* @param handler the bean name of a handler or a handler instance
* handler可能是bean名称
*/
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType =
(handler instanceof String ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
// Avoid repeated calls to getMappingForMethod which would rebuild RequestMatchingInfo instances
final Map<Method, T> mappings = new IdentityHashMap<Method, T>();
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 猜测这里的处理应该是挑出含有RequestMapping注解的方法,并建立起方法与RequestMappingInfo(包含请求url)之间的关系
Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() {
public boolean matches(Method method) {
T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
if (mapping != null) {
mappings.put(method, mapping);
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
});
for (Method method : methods) {
registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mappings.get(method));
}
}
/**
* Register a handler method and its unique mapping.
* 建立起handler method与RequestMappingInfo之间的匹配关系
* @param handler the bean name of the handler or the handler instance
* @param method the method to register
* @param mapping the mapping conditions associated with the handler method
* @throws IllegalStateException if another method was already registered
* under the same mapping
*/
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = this.handlerMethods.get(mapping);
if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() +
"' bean method \n" + newHandlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already '" +
oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method\n" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped.");
}
// handlerMethods是一个map,之后通过mapping在handlerMethods中可以找到handler method
this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + newHandlerMethod);
}
Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping);
for (String pattern : patterns) {
if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) {
// urlMap也是一个map,之后通过url可以在urlMap中找到对应的mapping
this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping);
}
}
}
}
就是通过上面的过程,在RequestMappingHandlerMapping中建立起了handler method与mapping之间的匹配关系。需要注意的一点是建立此映射关系时默认只会扫描子WAC中的bean,建立其中包含的Controller中的url与对应处理方法之间的对应关系,所以对于Controller类的扫描最好放在子WAC中进行,否则会导致映射关系建立失败。如果实在想要扫描父WAC中的Controller,需要设置相应的HandlerMapping中的detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts属性为true。
上面分析完了HandlerMapping的初始化过程,接下来就来看看SpringMVC对Web请求处理过程,我们从HTTPServlet的service方法开始分析:
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
// 以get请求为例进行分析
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
}
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean {
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
...
try {
// 调用DispatcherServlet的doService方法
doService(request, response);
}
...
}
}
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
/** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet */
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch}
* for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
...
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* 分发请求到对应的handler(Controller)
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* 将会依次遍历HandlerMapping,获取url对应的handler
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* 通过当前servlet安装的HandlerAdapters中获取第一个支持这个handler类的HandlerAdapter
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* 所有的HTTP请求都被这个方法处理,由HandlerAdapters或handlers本身来决定哪个方法是可接受的
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 对于当前request,为其找到对应的HandlerExecutionChain进行处理
// HandlerExecutionChain中含有拦截器interceptors和对应的handler(Controller)
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
...
}
@Deprecated
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request, boolean cache) throws Exception {
return getHandler(request);
}
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
* 顺序尝试每个HandlerMapping,看哪个符合要求
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
}
以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例介绍getHandler方法:
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered {
/**
* Look up a handler for the given request, falling back to the default
* handler if no specific one is found.
* 对于给定request,查找符合要求的handler,如果没有,使用默认handler
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the corresponding handler instance, or the default handler
* @see #getHandlerInternal
*/
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取的handler实际是一个HandlerMethod对象
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 将handler method与interceptor对象结合起来,建立起HandlerExecutionChain对象返回
return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
}
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
chain.addInterceptors(getAdaptedInterceptors());
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor : this.mappedInterceptors) {
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
return chain;
}
}
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
/**
* Look up a handler method for the given request.
* 对于给定request,查找符合要求的handler
*/
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
// 根据路径查找匹配的handlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
}
else {
logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
/**
* Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request.
* If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected.
* @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping
* @param request the current request
* @return the best-matching handler method, or {@code null} if no match
* @see #handleMatch(Object, String, HttpServletRequest)
* @see #handleNoMatch(Set, String, HttpServletRequest)
*/
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 匹配当前lookupPath的mappings可能有多个,需要找出匹配最精确的一个
List<T> directPathMatches = this.urlMap.get(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.handlerMethods.keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
// 排序后第0个就是匹配的最精确的
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
// 存在两个匹配同样精确的handler method,则抛出异常
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" + request.getRequestURL() + "': {" +
m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(handlerMethods.keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
// 通过在handlerMethods根据mapping获取对应的handlerMethod建立Match
matches.add(new Match(match, this.handlerMethods.get(mapping)));
}
}
}
private class Match {
private final T mapping;
private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
public Match(T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
this.mapping = mapping;
this.handlerMethod = handlerMethod;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.mapping.toString();
}
}
}
介绍完了DispatcherServlet中doDispatch()方法为request查找handlerExecutorChain的过程之后,继续来看doDispatch()方法:
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* 分发请求到对应的handler(Controller)
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* 将会依次遍历HandlerMapping,获取url对应的handler
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* 通过当前servlet安装的HandlerAdapters中获取第一个支持这个handler类的HandlerAdapter
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* 所有的HTTP请求都被这个方法处理,由HandlerAdapters或handlers本身来决定哪个方法是可接受的
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 对于当前request,为其找到对应的HandlerExecutionChain进行处理
// HandlerExecutionChain中含有拦截器interceptors和对应的handler(Controller)
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 根据找到的handler获取其对应的HandlerAdapter,以RequestMappingHandlerAdapter为例进行接下来的介绍
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 执行mappedHandler中interceptors中的前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 使用HandlerAdapter进行实际的处理操作,也就是在这里调用了我们提供的Controller中的处理方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(request, mv);
// 执行mappedHandler中interceptors中的后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Error err) {
triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object.
* @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for
* handler可能是一个HandlerMethod类的实例,这里HandlerAdapter的设计与Spring AOP模块中的AdviceAdapter有异曲同工之妙
* @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error.
*/
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
}
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter extends WebContentGenerator implements HandlerAdapter, Ordered {
/**
* This implementation expects the handler to be an {@link HandlerMethod}.
* 这个方法实现要求handler是一个HandlerMethod类的实例
*/
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
}
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
@Override
protected final ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
// Always prevent caching in case of session attribute management.
checkAndPrepare(request, response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers, true);
}
else {
// Uses configured default cacheSeconds setting.
checkAndPrepare(request, response, true);
}
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
return invokeHandleMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
}
// 继续调用处理
return invokeHandleMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
/**
* Invoke the {@link RequestMapping} handler method preparing a {@link ModelAndView}
* if view resolution is required.
*/
private ModelAndView invokeHandleMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
...
// 继续调用处理
requestMappingMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
public final void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 继续调用InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest处理
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
...
}
}
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
/**
* Invoke the method after resolving its argument values in the context of the given request.
* <p>Argument values are commonly resolved through {@link HandlerMethodArgumentResolver}s.
* The {@code providedArgs} parameter however may supply argument values to be used directly,
* i.e. without argument resolution. Examples of provided argument values include a
* {@link WebDataBinder}, a {@link SessionStatus}, or a thrown exception instance.
* Provided argument values are checked before argument resolvers.
* @param request the current request
* @param mavContainer the ModelAndViewContainer for this request
* @param providedArgs "given" arguments matched by type, not resolved
* @return the raw value returned by the invoked method
* @exception Exception raised if no suitable argument resolver can be found,
* or if the method raised an exception
*/
public final Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
...
Object returnValue = doInvoke(args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method [" + getMethod().getName() + "] returned [" + returnValue + "]");
}
return returnValue;
}
/**
* Invoke the handler method with the given argument values.
*/
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod());
try {
// 获取handlerMethod对应的bean,准备反射调用handlerMethod并传入相应请求参数
return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args);
}
...
}
}
package java.lang.reflect;
public final class Method extends Executable {
@CallerSensitive
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
...
// 之后就是通过这样的层层调用,最终反射调用obj.handlerMethod并传入相应请求参数
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
}
到此为止,SpringMVC初始化及web请求转发原理已经介绍完了,最后做一个总结。
总结
本篇文章从在Web环境中建立Spring IOC容器的实现原理开始入手,先分析了Spring IOC容器在Web容器中的配置和初始化完成过程。从整个体系上看,这些web应用可以看成是一个Spring应用,与一般的Spring应用并无太大的差别,都需要配置IOC容器和各种Bean定义,在理解了SpringIOC容器实现原理的基础上,这些内容并不难理解,只是因为Web容器存在一定的特殊性,所以在配置方面需要使用Spring作为平台的web应用有一些与Web环境相对应的特殊处理,比如对Servlet和ServletContext的使用等。
之后分析了DispatcherServlet初始化的过程,在这个过程中,它以根WebApplicationContext作为父容器建立了子容器,并通过监听ContextRefreshedEvent获取相应HandlerMapping实例准备对Web请求进行处理,在HandlerMapping实例被创建的过程中,在其中会建立起url与handler之间的对应关系,之后请求到来就可以获取到相应的handler进行处理。
之后Web请求到来,DispatcherServlet会根据具体的URL请求信息在HandlerMapping中进行查询,从而得到相应的HandlerExecutionChain,其中封装了对于interceptors和Controller中的handlermethod,之后先调用interceptors的前置处理,然后是由HandlerAdapter反射调用Controller的handlerMethod,然后是调用interceptors的后置处理,最后将响应数据返回给用户。
在上面对SpringMVC框架的分析过程中,可以看到SpringMVC很好的提供了与web环境中的IOC容器的集成,在其功能实现中使用了IOC容器的许多特性。
(完)